装备

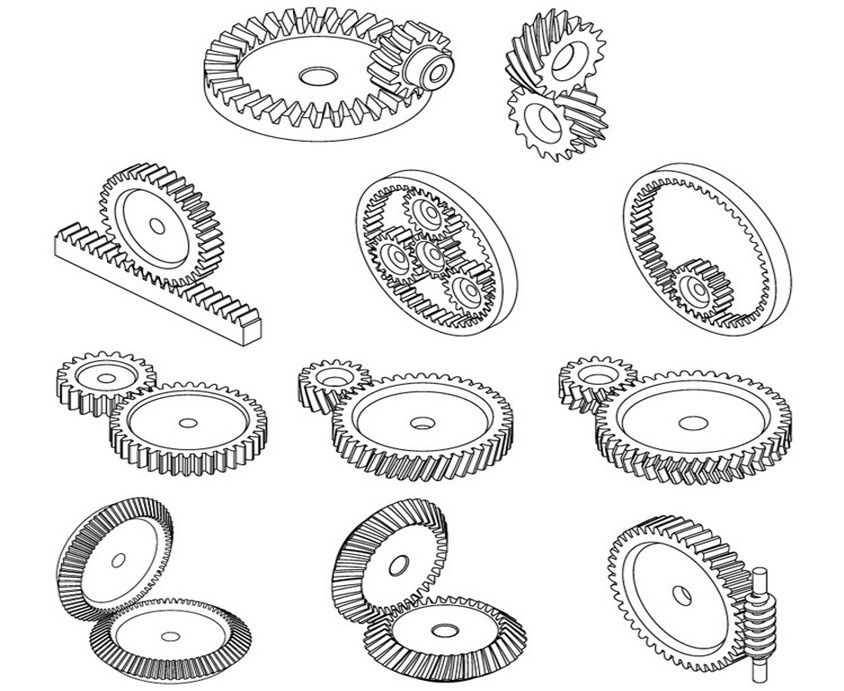
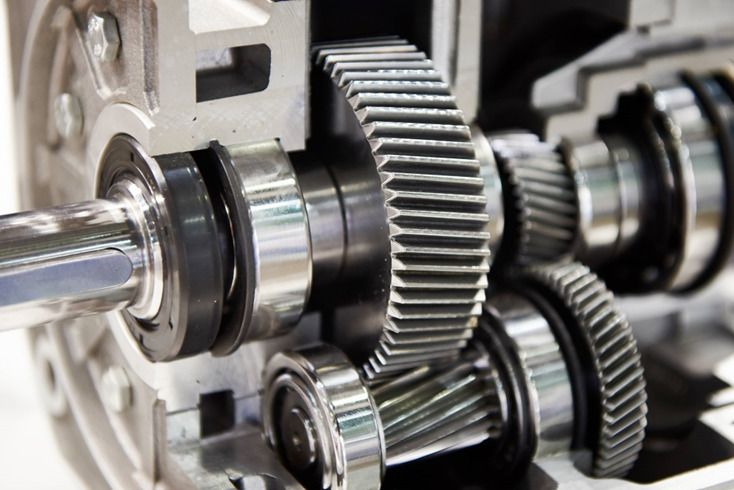
Spur Gears
The most common type of gears employed, spur gears are constructed with straight teeth cut or inserted parallel to the gear’s shaft on a circular (i.e., cylindrical) gear body. In mated pairs, these gears employ the parallel axes configuration to transmit motion and power. Depending on the application, they can be mated with another spur gear, an internal gear (such as in a planetary gear system), or a gear rack (such as in a rack and pinion gear pair).
The simplicity of the spur gear tooth design allows for both a high degree of precision and easier manufacturability. Other characteristics of spur gears include lack of axial load (i.e., the thrust force parallel to the gear shaft), high-speed and high-load handling, and high efficiency rates. Some of the disadvantages of spur gears are the amount of stress experienced by the gear teeth and noise produced during high-speed applications.
This type of gear is used for a wide range of speed ratios in a variety of mechanical applications, such as clocks, pumps, watering systems, power plant machinery, material handling equipment, and clothes washing and drying machines. If necessary for an application, multiple (i.e., more than two) spur gears can be used in a gear train to provide higher gear reduction.
螺旋齿轮
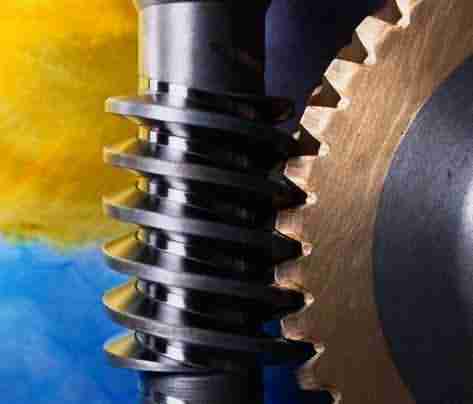
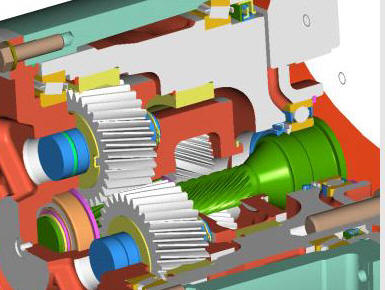
Similar to spur gears, helical gears typically employ the parallel axes configuration with mated gear pairs, but, if aligned properly, they can also be used to drive non-parallel, non-intersecting shafts. However, unlike spur gears, these gears are constructed with teeth which twist around the cylindrical gear body at an angle to the gear face. Helical gears are produced with right-hand and left-hand angled teeth with each gear pair comprised of a right-hand and left-hand gear of the same helix angle.
The angled design of helical teeth causes them to engage with other gears differently than the straight teeth of spur gears. As properly matched helical gears come in contact with one another, the level of contact between corresponding teeth increases gradually, rather than engaging the entire tooth at once. This gradual engagement allows for less impact loading on the gear teeth and smoother, quieter operation. Helical gears are also capable of greater load capabilities but operate with less efficiency than spur gears. Further disadvantages include the complexity of the helical tooth design, which increases the degree of difficulty in its manufacturing (and, consequently, the cost) and the fact that the single helical gear tooth design produces axial thrust, which necessitates the employment of thrust bearings in any application which uses single helical gears. This latter necessity further increases the total cost of using helical gears.
|
Type of Gear |
特征 |
|
Spur |
|
|
Helical |
|
|
Bevel |
|
|
Worm |
|
|
Rack and Pinion |
|
Bevel Gears
Bevel gears are cone-shaped gears with teeth placed along the conical surface. These gears are used to transmit motion and power between intersecting shafts in applications which require changes to the axis of rotation. Typically, bevel gears are employed for shaft configurations placed at 90-degree angles, but configurations with lesser or greater angles are also manageable.
There are several types of bevel gears available differentiated mainly by their tooth design. Some of the more common types of bevel gears include straight, spiral, and hzpt bevel gears.
Straight Bevel Gears
The most commonly used of the bevel gear tooth designs due to its simplicity and, consequently, its ease of manufacturing, straight bevel teeth are designed such that when properly matched straight bevel gears come into contact with one another, their teeth engage together all at once rather than gradually. As is the issue with spur gears, the engagement of straight bevel gear teeth results in high impact, increasing the level of noise produced and amount of stress experienced by the gear teeth, as well as reducing their durability and lifespan.
Spiral Bevel Gears
In spiral bevel gears, the teeth are angled and curved to provide for more gradual tooth engagement and more tooth-to-tooth contact than with a straight bevel gear. This design greatly reduces the vibration and noise produced, especially at high angular velocities (>1,000 rpm). Like helical gears, spiral bevel gears are available with right-hand or left-hand angled teeth. As is also the case with helical gears, these gears are more complex and difficult to manufacture (and, consequently, more expensive), but offer greater tooth strength, smoother operation, and lower levels of noise during operation than straight bevel gears.
为什么选择我们?
(1) 我们提供 OEM 服务,向客户提供各种款式和最新设计;
(2) 我们与东南亚、非洲、中东、北美和南美的主要客户开展合作;
(3)根据不同地区客户的需求,我们为您配套了各种款式的减速机,使客户在市场上具有极大的竞争力!
(4) 我们拥有 20 多年为客户提供优质产品和最专业服务的丰富经验!
(5) 我们可以灵活地从中国任何港口出口货物!欢迎您前来咨询!
公司优势:
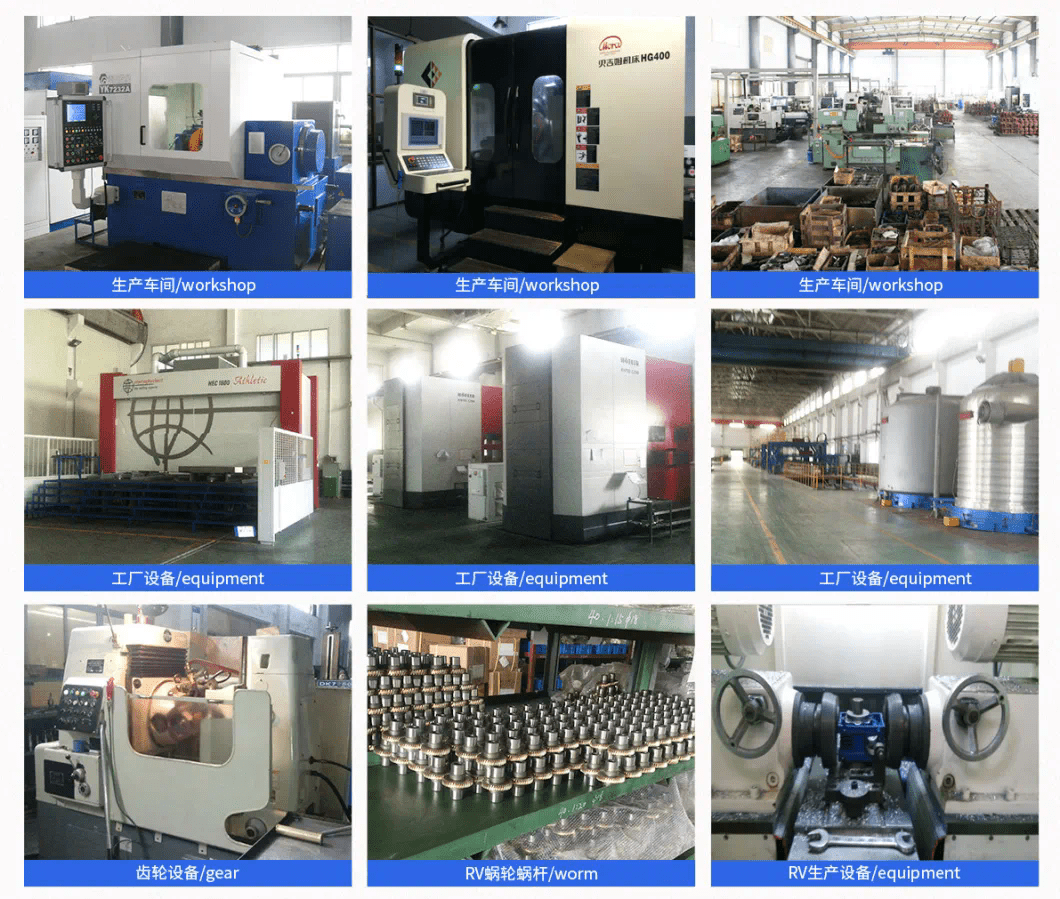
1.生产能力大,交货快。
2.严格的质量控制检验规则:所有产品必须通过 100% 检验方可出厂。
3.提供 OEM/ODM 服务
4.24 小时在线服务。
5.实时报价查询
6.高质量、高可靠性、产品寿命长。
7.专业制造商提供有竞争力的价格。
8.多元化、经验丰富的技术工人。
质量管理系统:
在 HZPT,产品和服务质量是重中之重。
我们的员工接受有关质量方法和原则的培训。
在组织的各个层面,我们都致力于提高产品质量和改进工艺流程。
这种深刻的承诺帮助我们赢得了客户的信任,成为世界首选品牌。
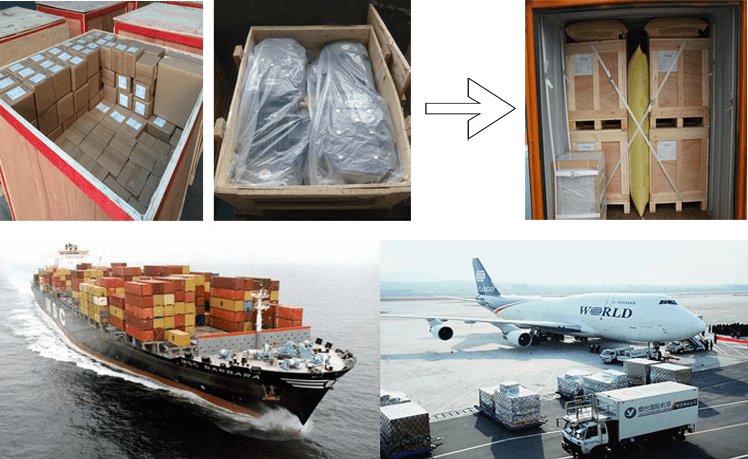
包装和交货时间
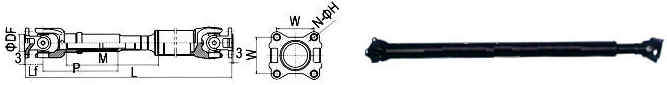
尺寸图纸
木箱/容器和托盘,或根据客户定制的规格。
样品 15-25 天。正式订单 30-45 天
港口:上海/宁波港
常见问题
常见问题:
致客户
从中国采购是否有利可图?
中国仍然是世界上最大的供应商之一。您所选择的产品在您的目标市场肯定是有利可图的,因为中国正以具有竞争力的质量和价格向全世界供应产品。
2) 我是否需要前往中国才能购买产品?
我们为您打点一切,让您节省机票、酒店和旅行费用。不过,如果您决定来中国旅游,我们会尽力为您安排舒适的住宿,让您有一个愉快的旅行体验。
3) 你们提供什么类型的产品?
种类繁多的工业、汽车和农业产品。每种产品都有专门的团队负责。
4) 从中国采购或与你们合作有什么风险?
您基本上没有任何风险。我们为您采购,您可以放心地接受我们的检验。如果您有时间来中国,可以在生产过程中访问我们。您可以使用我们的联系网络和销售团队。我们将认真对待您的产品。如果您不想出差,也不必出国,因为您在中国有知识渊博的合作伙伴。
5) 我可以自己找到产品供应商,为什么还需要你们?
您可以这样做。但是,您的投资会高得多。另外,您没有熟悉市场并能为您提供机会网络的本地合作伙伴。
要从中国购买产品,您需要在当地设立办事处,以便与供应商签订合同,还需要一个工程师团队,以便不时进行质量和数量检查。您需要了解原材料的来源,最重要的是避免任何外购。
6) 你们的结构如何?
我们有不同的部门,每个部门都在每个方面有所专长。我们可以提供物流协助、采购协助、检验协助和法律援助。
7) 这项服务是否只针对大公司?
不,我们确信,通过第一次合作,您会对与我们保持业务关系充满信心,因为我们的关系建立在诚信和互惠互利的基础上,所以您将来会扩大您的业务。我们关心您,让您比以前更加强大。我们将携手并进,不断壮大。
我们欢迎任何公司,无论规模大小,让我们携手共进 . .
如需了解更多信息,请发送电子邮件至



/helica1.jpg)