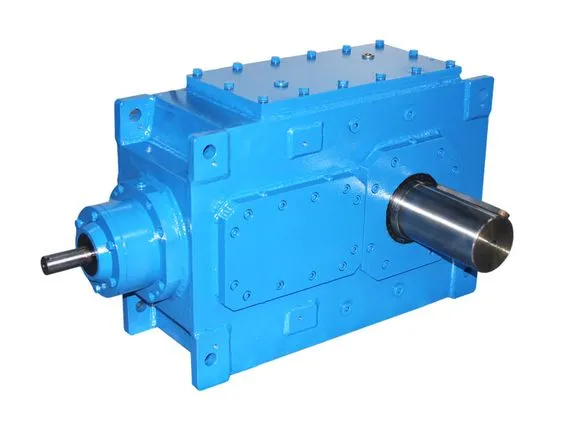
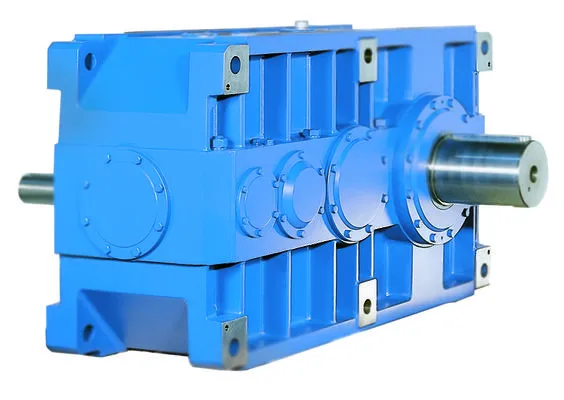
In the realm of mechanical engineering, gearboxes stand as pivotal components, bridging power sources to action. Among their diverse types, the parallel gearbox emerges as a marvel of engineering, offering unparalleled efficiency and adaptability. This guide delves into the world of parallel gearboxes, illuminating their structure, benefits, and applications.
Understanding Gearboxes
Basics of Gearboxes
Gearboxes are fundamental components in mechanical systems, playing a crucial role in transmitting power from an engine or motor to the machine it operates. By adjusting the output speed and torque of the driving device to match the requirements of the load, gearboxes enhance efficiency and performance in a wide array of applications, from automobiles and industrial machinery to household appliances and wind turbines. Understanding the basics of gearboxes involves grasping their function, types, and how they operate.
Function
The primary function of a gearbox is to change the speed and torque of a power source to align with the needs of a specific application. This process involves converting high-speed, low-torque (force) input into lower-speed, higher-torque output, or vice versa, depending on the requirements. Gearboxes enable machines to operate more effectively by providing the power needed at the optimal speed and force, thus significantly improving performance and reducing energy consumption.
Types of Gearboxes
Gearboxes are integral components in various machinery, facilitating the transmission of power from an engine to the device it operates. They modify torque and speed according to the needs of a system. Understanding the different types of gearboxes is essential for selecting the right one for any application. Here's an overview of the most common types:
Spur Gearboxes
- Characteristics: Spur gears have straight teeth parallel to the gearbox's axis. They are the simplest type of gearbox, known for their reliability and high power transmission efficiency.
- Applications: Widely used in low-speed or low-impact applications such as conveyors, cooling towers, and mechanical clocks.
Helical Gearboxes
- Characteristics: These gearboxes feature angled teeth, which allows for a gradual engagement between gears. This design reduces noise and vibration, making them suitable for high-speed applications.
- Applications: Helical gearboxes are preferred in automotive transmissions, elevators, and other machinery requiring quiet operation.
Bevel Gearboxes
- Characteristics: Bevel gears have conically shaped teeth and are mounted on intersecting axes, usually at a 90-degree angle. They are designed to change the direction of the shaft's rotation.
- Applications: Common in differential drives of vehicles, allowing wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, and in various industrial machines with angular configurations.
Worm Gearboxes
- Characteristics: A worm gearbox consists of a worm (similar to a screw) that meshes with a worm wheel (similar to a spur gear). This setup allows for high torque reduction and is self-locking in some configurations.
- Applications: Useful in heavy-duty applications like elevators, conveyors, and mining equipment, where compactness and safety are priorities.
Planetary Gearboxes
- Characteristics: Planetary gearboxes consist of a central sun gear, planet gears that rotate around it, and an outer ring gear. This configuration offers high torque transmission and efficiency in a compact size.
- Applications: Employed in automatic transmissions, electric screwdrivers, and applications requiring high torque and durability, such as robotics and aerospace.
Hypoid Gearboxes
- Characteristics: Hypoid gears are similar to bevel gears but with axes that do not intersect, allowing for larger diameter gears and more significant contact surfaces. This results in smoother operation and greater torque transmission.
- Applications: Primarily used in the automotive industry for rear axles of vehicles, offering improved efficiency and noise reduction.
Harmonic Gearboxes
- Characteristics: These gearboxes use a flexible output gear and a rigid circular spline to produce high reduction ratios in a very compact and lightweight package. They exhibit almost no backlash.
- Applications: Ideal for precision machinery, robotics, and aerospace applications where weight and space are critical, and high precision is required.
Sequential Gearboxes
- Characteristics: Sequential gearboxes allow the user to select gears in sequence, either up or down, without having to shift through intermediate gears. They provide rapid shifting.
- Applications: Commonly found in motorcycles and high-performance racing cars where quick gear changes are essential.
Each type of gearbox offers unique advantages and is suitable for specific applications based on requirements for speed, torque, direction of transmission, noise levels, and space constraints. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and designers to select the most appropriate gearbox for their needs.
What is a Parallel Gearbox?
A parallel gearbox is a sophisticated mechanical system designed to transmit power efficiently from a driving force to a driven mechanism. This type of gearbox is distinguished by its configuration of gears aligned on parallel shafts, enabling a seamless and direct flow of power within the system. The design is favored for its straightforward power transmission path, which contributes to its high efficiency and reliability in various applications.
Definition
At its core, a parallel gearbox is engineered to accommodate gears arranged in parallel to each other, ensuring that the rotational motion and power are transferred directly and efficiently from the input to the output. This arrangement is instrumental in machinery that requires a compact, efficient transmission system capable of handling high power levels without significant energy loss.
Components
The functionality and efficiency of a parallel gearbox depend on its critical components, each playing a vital role in the system's operation:
- Gears: Gears are the heart of any gearbox. In a parallel gearbox, these are the toothed wheels that mesh together to transmit power from the engine or motor to the machinery. The precision in the design and alignment of these gears is crucial for the smooth transfer of power and for minimizing wear and tear over time.
- Shafts: Shafts serve as the backbone of the gearbox, providing a sturdy axis around which the gears rotate. In parallel gearboxes, these shafts are aligned in a parallel configuration, ensuring that the gears mounted on them engage as intended. The shafts must be strong enough to withstand the torque transmitted through the gears without bending or breaking.
- Bearings: Bearings play a critical role in any gearbox by supporting the rotating shafts and gears, reducing friction, and facilitating smooth motion. They are strategically placed to handle the load and stresses exerted on the system, thereby extending the lifespan of the gearbox by preventing direct metal-on-metal contact.
Working Principle
The operation of a parallel gearbox is characterized by the linear flow of power through gears mounted on parallel shafts. When the input shaft, connected to the power source, begins to rotate, it drives the corresponding gear. This gear, in turn, meshes with and drives another gear on a different shaft, thereby transmitting power through the gearbox. This process can involve several gears and shafts, depending on the required speed and torque output.
The efficiency of a parallel gearbox lies in its direct transmission path, which minimizes mechanical losses. The parallel arrangement of shafts and gears ensures that energy is not wasted in unnecessary redirection or conversion, making these gearboxes an excellent choice for applications requiring high efficiency and reliability. Their straightforward design also simplifies maintenance and reduces the risk of operational failures, making parallel gearboxes a dependable component in various mechanical systems.
Applications of Parallel Gearboxes
Parallel gearboxes are integral components in a vast array of applications across multiple industries. Their unique design, which allows for efficient power transmission and minimal energy loss, makes them particularly versatile and suited for tasks requiring reliability and endurance. Here's a closer look at some specific applications of parallel gearboxes, highlighting their importance and utility in different sectors:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, parallel gearboxes play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles. They are commonly used in the drivetrain systems of cars, trucks, and motorcycles, where they facilitate the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. By enabling precise control over the speed and torque of a vehicle, parallel gearboxes contribute significantly to the performance, fuel efficiency, and overall driving experience.
Manufacturing Plants
Manufacturing facilities rely heavily on machinery and equipment that are capable of continuous operation under high-stress conditions. Parallel gearboxes are employed in various machines, including conveyors, mixers, presses, and assembly lines, to provide the necessary power transmission capabilities. Their robustness and reliability make them ideal for applications that demand consistent performance and minimal downtime.
Agricultural Machinery
The agriculture industry benefits from the use of parallel gearboxes in a variety of farming equipment, such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems. These gearboxes enable the machinery to operate under varying loads and conditions, ensuring that tasks like plowing, seeding, and harvesting can be performed efficiently and effectively.
Renewable Energy Systems
Parallel gearboxes are also pivotal in the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines. They are used to convert the low-speed, high-torque rotation of the turbine blades into a higher speed rotation suitable for generating electricity. The durability and efficiency of parallel gearboxes make them suitable for this application, where they must withstand variable and often harsh environmental conditions.
Marine and Offshore Applications
In the marine industry, parallel gearboxes are found in propulsion systems of ships and boats, where they help regulate the speed and direction of travel. They are also used in offshore platforms and equipment for oil and gas exploration and extraction, providing the necessary power transmission solutions in these challenging environments.
Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense industries utilize parallel gearboxes in various applications, from aircraft propulsion systems to ground support equipment. The high precision and reliability required in these sectors make parallel gearboxes a preferred choice for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of equipment.
Entertainment Industry
Parallel gearboxes find unexpected applications in the entertainment industry as well, particularly in theme park rides and stage equipment. They are used to control motion and speed, contributing to the safety and enjoyment of these attractions.
These examples illustrate the versatility and critical importance of parallel gearboxes across a broad spectrum of industries. Their ability to transmit power efficiently, combined with their durability and reliability, makes them indispensable components in modern mechanical systems.
Advantages of Parallel Gearboxes
Parallel gearboxes stand out in the world of mechanical engineering for their distinct advantages, which stem from their unique design and operational characteristics. These advantages not only contribute to their widespread application across various industries but also make them a preferred choice for many power transmission needs. Let's delve deeper into the benefits of parallel gearboxes:
Efficiency
One of the most notable advantages of parallel gearboxes is their high efficiency in power transmission. The parallel arrangement of the gears allows for a more straightforward and direct flow of power from the input to the output shaft without unnecessary diversions or conversions. This efficiency in design minimizes energy loss during operation, translating to significant energy savings over time. In applications where energy costs can accumulate, such as in large manufacturing plants or renewable energy systems, the use of parallel gearboxes can lead to substantial reductions in operational expenses.
Durability and Maintenance
Parallel gearboxes are renowned for their exceptional durability and low maintenance requirements. The robustness of their construction, coupled with the simplicity of their design, means that there are fewer moving parts susceptible to wear and tear. This durability ensures that parallel gearboxes can withstand the rigors of continuous, heavy-duty operation without frequent breakdowns. Moreover, their minimal maintenance needs stem from this straightforward design, which is easier to inspect, clean, and repair when necessary. This reliability and ease of maintenance contribute to lower overall lifecycle costs, making parallel gearboxes a cost-effective solution for many businesses.
Versatility
The versatility of parallel gearboxes is another significant advantage, allowing them to serve a broad spectrum of industries and applications. From automotive drivetrains and agricultural machinery to wind turbines and marine propulsion systems, parallel gearboxes can be found in an array of settings. This versatility is partly due to their ability to be tailored to meet specific power transmission requirements. Whether the need is for high torque output, precise speed control, or operation under extreme environmental conditions, parallel gearboxes can be designed and manufactured to suit these diverse requirements. Their adaptability makes them an invaluable component in the design and operation of a wide variety of mechanical systems.
Additional Considerations
Beyond the primary benefits, parallel gearboxes also offer other advantages, such as reduced noise levels compared to other gearbox types. Their design can be optimized to minimize gear meshing noise, making them suitable for applications where noise reduction is a priority. Furthermore, their compact size relative to their power transmission capabilities means that they can be easily integrated into space-constrained environments, adding to their versatility.
In summary, the advantages of parallel gearboxes—ranging from their efficiency and durability to their versatility—make them an essential component in various mechanical systems. Their ability to provide reliable, cost-effective power transmission solutions across a wide range of applications underscores their importance in modern engineering and industrial operations.
Choosing the Right Parallel Gearbox
Choosing the right parallel gearbox is a critical decision in the design and operation of mechanical systems, impacting efficiency, reliability, and overall performance. To make an informed choice, several key considerations must be taken into account, ensuring the selected gearbox aligns perfectly with system requirements and operational conditions. Here's an expanded view on the essential factors and tips for selecting the ideal parallel gearbox:
Considerations
Power Needs
The foremost consideration is the power requirement of your system. Parallel gearboxes are available in various capacities, designed to handle a wide range of power outputs. It's crucial to understand the maximum power your system will need, including any potential peaks in demand, to ensure the gearbox can handle it without risk of failure or undue wear.
Desired Speed Ratios
The speed ratio, or the difference between the input and output speeds, is a key factor in selecting a gearbox. Determine the speed at which your machinery operates and what input speed is available from your power source. This ratio will guide you in choosing a gearbox that can adequately reduce or increase speed to meet your operational needs.
Operational Conditions
The environment in which the gearbox will operate can significantly affect its performance and longevity. Factors such as temperature, presence of corrosive substances, and the potential for shock or vibration should be considered. Gearboxes are designed with certain operational conditions in mind, so selecting one that matches your specific environment is essential for optimal performance and durability.
Tips for Selection
Prioritize Compatibility
Compatibility with your system's requirements is paramount. This means not only ensuring the gearbox can handle the mechanical demands of your operation but also that its physical dimensions fit within your system's design. The alignment of shafts, mounting configurations, and connections to power sources and driven components must be considered to ensure seamless integration.
Consider Environmental Factors
The operating environment can greatly affect the choice of materials and seals used in the gearbox. For applications in harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or exposure to corrosive elements, choosing a gearbox with appropriate protective measures (such as corrosion-resistant materials or specialized seals) is crucial. This consideration can prevent premature failure and extend the service life of the gearbox.
Evaluate Efficiency and Reliability
Efficiency and reliability are key attributes that can vary between gearbox models and manufacturers. Reviewing performance data and reliability statistics, as well as seeking out user testimonials or industry recommendations, can provide valuable insights. Selecting a highly efficient and reliable gearbox can lead to lower energy costs and reduced downtime, contributing to the overall success of your operation.
Seek Expert Advice
When in doubt, consulting with experts or the gearbox manufacturers can provide clarity and guidance. These professionals can offer personalized advice based on a comprehensive understanding of your needs and the challenges of your specific application. Their expertise can be invaluable in navigating the selection process and ensuring you choose the most suitable parallel gearbox for your requirements.
In summary, selecting the right parallel gearbox involves a careful evaluation of your system's power needs, desired speed ratios, and operational conditions. By prioritizing compatibility, considering environmental factors, and focusing on efficiency and reliability, you can ensure that your chosen gearbox will support optimal performance and durability in your mechanical system.
Maintenance Tips for Parallel Gearboxes
Maintaining a parallel gearbox in optimal working condition is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of both the gearbox and the machinery it operates. A well-maintained gearbox can prevent costly downtime and repairs, making regular maintenance practices invaluable. Here are expanded and detailed maintenance tips for parallel gearboxes:
Regular Lubrication
Lubrication is the lifeblood of any gearbox, reducing friction between moving parts, minimizing wear, and dissipating heat. For parallel gearboxes:
- Choose the Right Lubricant: Select a lubricant that matches the manufacturer's specifications and is suitable for your operational environment. Consider viscosity, compatibility with gearbox materials, and any special properties needed for extreme temperatures or conditions.
- Schedule Regular Lubrication: Establish a regular lubrication schedule based on operational hours and manufacturer recommendations. Over-lubrication can be as detrimental as under-lubrication, causing excessive pressure that can lead to seal failure.
- Monitor Lubricant Condition: Check the condition of the lubricant regularly for signs of contamination, degradation, or loss of viscosity. Changes in lubricant condition can indicate issues within the gearbox.
Routine Inspections
Regular inspections can identify potential issues before they lead to failure:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect the gearbox exterior for signs of oil leaks, damage, or wear. Pay special attention to seals and gaskets.
- Auditory Checks: Listen for unusual noises during operation, such as grinding, knocking, or whining, which can indicate internal issues like misalignment or bearing failure.
- Vibration Analysis: Implement vibration analysis to detect abnormalities that could suggest misalignment, imbalance, or wear. Early detection of such issues can prevent more significant problems.
Wear Checks
Component wear is inevitable over time but can be managed through regular checks:
- Gear Teeth: Check for wear patterns, chipping, or breakage on the gear teeth. Uneven wear patterns can indicate alignment issues or improper loading.
- Bearings: Inspect bearings for signs of wear or damage. Worn bearings can cause misalignment and excessive vibration, leading to further damage.
- Shafts: Examine shafts for signs of wear, corrosion, or distortion. Shafts in poor condition can affect the overall operation of the gearbox.
Additional Maintenance Tips
- Keep Records: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, lubrication, and any repairs or replacements. This history can be invaluable for troubleshooting and planning future maintenance.
- Cleanliness: Keep the gearbox and its environment clean to prevent dirt or debris from entering the system, which can cause abrasion and premature wear.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitor the operating temperature of the gearbox. Excessive heat can be a sign of overloading, insufficient lubrication, or internal wear.
- Professional Assistance: For complex issues or when performing major maintenance tasks, don't hesitate to seek professional help. Expertise in gearbox maintenance can ensure that the work is done correctly and safely.
Adhering to these maintenance tips can significantly extend the lifespan of a parallel gearbox, ensuring it continues to operate efficiently and reliably. Regular care not only safeguards the gearbox itself but also contributes to the smooth operation of the broader mechanical system it serves.
Conclusion
Parallel gearboxes stand out for their efficiency, durability, and broad applicability. Whether you're involved in automotive, aerospace, or manufacturing sectors, incorporating a parallel gearbox could significantly enhance your mechanical systems.